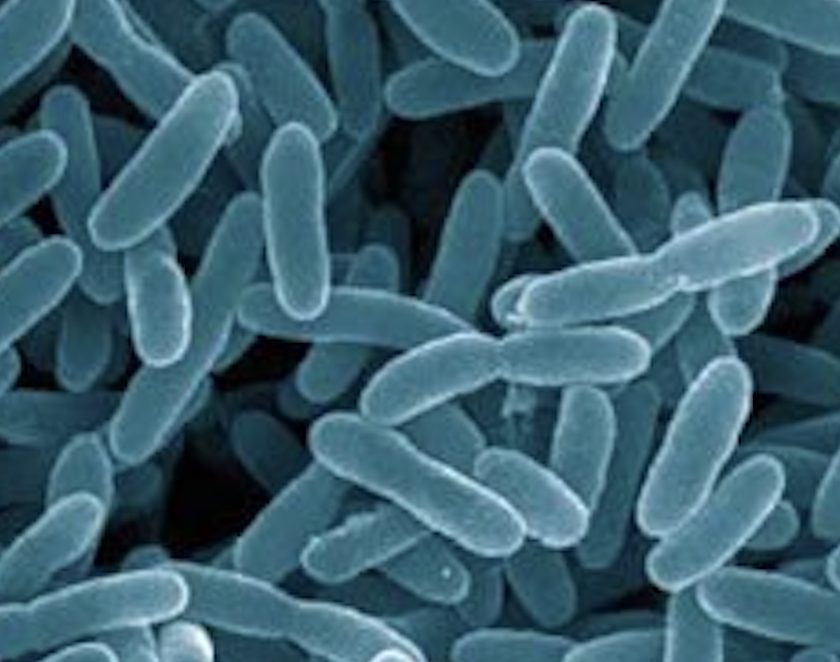
Proteobacteria
Proteobacteria is a phylum of bacteria that ranges from commensal bacteria to pathogenic bacteria.
Taxonomic Level: Phlyum
Properties: Gram-negative
Additional Information: Proteobacteria is the most diverse phylum with many pathogens including Escherichia (E. coli), Salmonella, Vibrio, and Helicobacter. Therefore, a high abundance of Proteobacteria are generally found in patients with metabolic diseases, inflammatory bowel diseases, and irritable bowel syndrome. Additionally, Proteobacteria is a Sulphate Reducing Bacteria- which produces hydrogen sulfide; hydrogen sulfide is toxic outside of healthy levels and can cause colonocyte apoptosis, degradation of mucous, and can inhibit butyrate production (please see the functional analysis section of your report to learn more about hydrogen sulfide). Butyrate is a short chain fatty acid which has many beneficial health implications, including protection against inflammatory bowel disease, diabetes, obesity, and cancer (please see the functional analysis section of your report to learn more about butyrate).
.png?width=3000&height=1170&name=NirvanaBiome_logo_fullcolor_RGB-1500%20(1).png)
.png?width=1500&height=585&name=NirvanaBiome_logo_fullcolor_RGB-1500%20(1).png)